Articles / Healthy Living
Jan 18, 2025
17K Views
Lectins 101: Are They Really That Bad for You?
By Food Matters Institute
Lectins have become a buzzword in nutrition circles, often painted as dietary villains. But what are lectins, and should you really be worried about them? Let’s dive into the science to separate fact from fiction and help you make informed decisions for your health.
What Are Lectins?
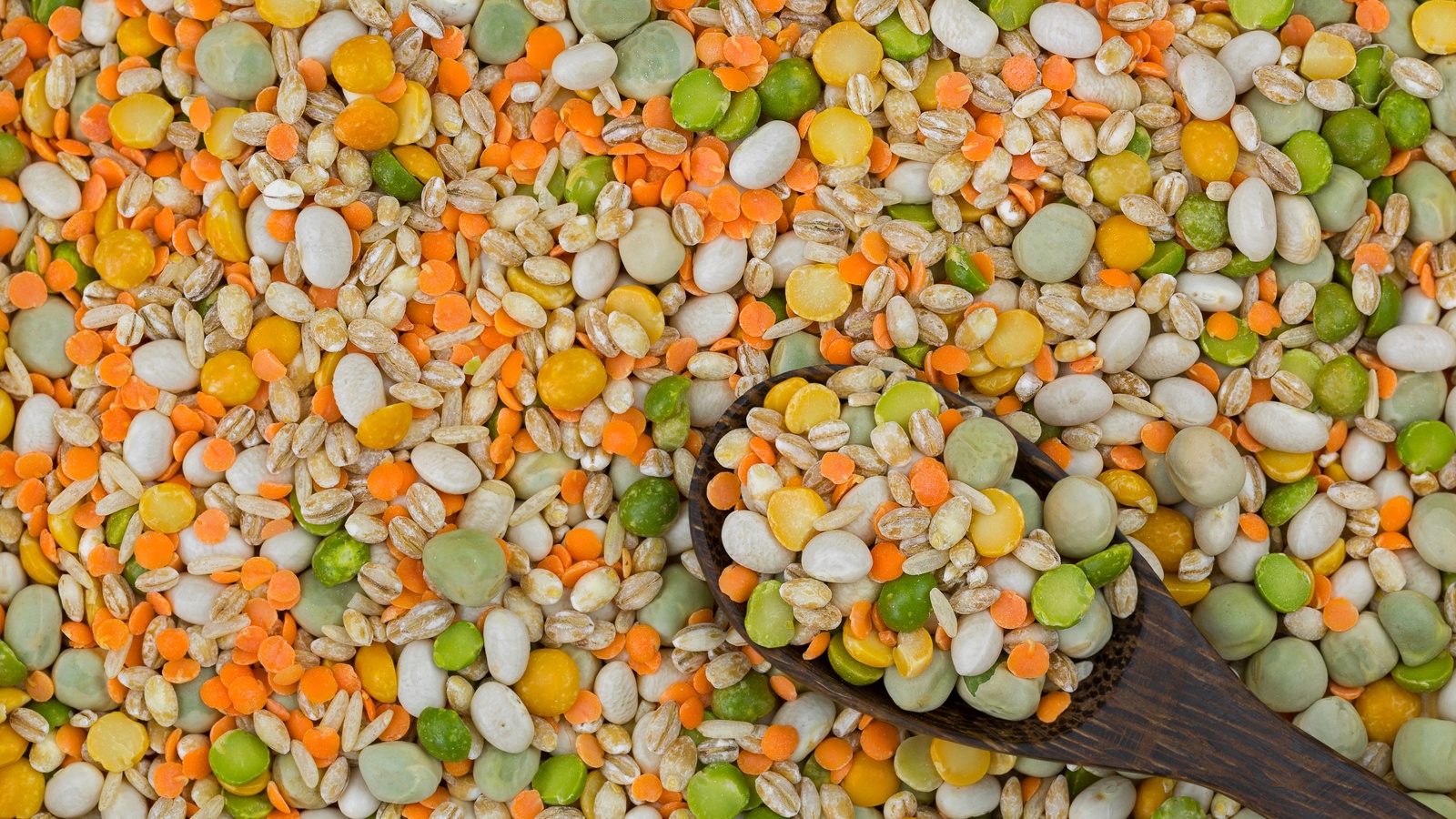
Lectins are a type of protein found in many plants, acting as a natural defense mechanism against predators. They bind to carbohydrates, which can affect how nutrients are absorbed in the gut. Common foods that contain lectins include beans, lentils, grains, tomatoes, and even some fruits.
While lectins serve a protective role for plants, their impact on humans is more nuanced. In large amounts or improperly prepared, certain lectins can cause digestive discomfort or interfere with nutrient absorption. However, most of the lectins we consume are rendered harmless through proper cooking and preparation.
The Concerns Around Lectins
Lectins have been criticized for their potential to:
-
Disrupt Digestion: Some lectins, like those in raw or undercooked kidney beans, can cause gastrointestinal upset.
-
Impact Nutrient Absorption: By binding to nutrients, lectins may reduce the availability of essential vitamins and minerals.
-
Trigger Inflammation: In sensitive individuals, lectins may exacerbate gut permeability or contribute to inflammatory responses.
These concerns have led to lectins being labeled as "anti-nutrients." However, this perspective often overlooks the broader nutritional value of lectin-containing foods.
The Health Benefits of Lectin-Containing Foods
Many foods high in lectins are also rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For example:
-
Beans and Lentils: Excellent sources of plant-based protein and folate.
-
Whole Grains: Packed with fiber that supports gut health and cardiovascular function.
-
Tomatoes and Peppers: Loaded with vitamin C and beneficial phytochemicals.
Eliminating these foods entirely may deprive you of their health benefits, which often outweigh the risks when they are prepared correctly.
How to Safely Consume Lectins
The key to enjoying lectin-containing foods is proper preparation:
-
Cook Thoroughly: Heat destroys most lectins. Boiling beans and grains, for instance, significantly reduces their lectin content.
-
Soak and Rinse: Soaking beans and grains before cooking can help break down lectins and improve digestibility.
-
Ferment: Fermentation processes, like those used to make sourdough bread, can reduce lectin levels.
-
Sprout: Sprouting grains and legumes lowers lectin content and boosts nutrient availability.
Are Lectins Right for You?
For most people, the benefits of lectin-containing foods far outweigh the risks. However, individuals with specific sensitivities, autoimmune conditions, or gut health issues may find reducing lectins beneficial. Working with a healthcare provider or nutrition coach can help determine what works best for your body.
Lectins are a natural component of many healthy foods and are not inherently "bad." The fear surrounding them is often overblown, overshadowing their nutritional benefits. By focusing on preparation methods and listening to your body, you can enjoy a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods without unnecessary worry.
At Food Matters Institute, we aim to empower you with balanced, evidence-based insights to guide your health journey. Remember, nutrition is about context, balance, and what feels right for you.